Spring에서 커스텀 예외를 다루는 방법
Spring에서 커스텀 예외를 다루는 방법
- 문제
- Spring의 예외 처리 흐름
- Spring이 제공하는 다양한 예외처리
문제
스프링으로 프로젝트를 진행하다 보면 예외 처리를 해야하는 경우 기본적으로 런타임 예외로 에러를 발생
하지만 런타임 예외가 아닌 커스텀 예외를 통해서 에러를 발생시키고, 커스텀 예외에 대해 클라이언트에게 명확한 에러 응답을 전달하고 싶다면, 스프링에서 제공하는 예외 처리 방법을 활용 가능
Spring의 예외 처리 흐름
요청(Request) 흐름
일반적으로 요청이 들어오면 다음과 같이 흐름
WAS(Tomcat) → Filter → Dispatcher Servlet → Interceptor → Controller
만약 컨트롤러 이하에서 예외가 발생하면 다음과 같이 흐름
Exception → Controller → Interceptor → Dispatcher Servlet → Filter → WAS(Tomcat)
이때 WAS는 스프링 부트가 등록한 에러 설정(/error)에 맞게 다음과 같이 에러 요청
WAS(Tomcat) → Filter → Dispatcher Servlet → Interceptor → BasicErrorController
즉 일반적인 요청에 의해 예외가 발생했을 때 기본적인 예외 처리는 전체적으로 다음과 같이 흐름
WAS(Tomcat) → Filter → Dispatcher Servlet → Interceptor → Controller → Exception → Controller → Interceptor → Dispatcher Servlet → Filter → WAS(Tomcat) → Filter → Dispatcher Servlet → Interceptor → BasicErrorController
BasicErrorController의 동작과 에러 속성들
헤더에 따라 에러 페이지를 반환하거나 에러 메세지를 반환
경로는 기본적으로 /error로 정의되어 있으며, properties에서 server.error.path로 변경 가능
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
...
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
...
}
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
...
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
...
}
errorHtml()과 error()는 모두 getErrorAttributeOptions를 호출해 기본적으로 DefaultErrorAttributes로부터 반환할 다음과 같은 에러 속성 정보를 받음
- timestamp: 에러가 발생한 시간
- status: 에러의 Http 상태
- error: 에러 코드
- path: 에러가 발생한 uri
- exception: 최상위 예외 클래스의 이름(설정 필요)
- message: 에러에 대한 내용(설정 필요)
- errors: BindingExecption에 의해 생긴 에러 목록(설정 필요)
- trace: 에러 스택 트레이스(설정 필요)
{
"timestamp": "2023-03-25T09:50:23.675+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"path": "/product/5000"
}
기본 설정으로 받는 에러 응답, 클라이언트 입장에서 충분하지 못한 정보로 인해 유용하지 못함
status가 500인 이유는 에러가 처리되지 않고 WAS가 에러를 전달받았기 때문
다음과 같이 properties.yml 통해 설정 가능
server:
error:
include-message: always
include-binding-errors: always
include-stacktrace: always
include-exception: true
하지만 설정을 변경했음에도 불구, status는 여전히 500, 유의미한 에러 응답을 전달하지 못함
{
"timestamp": "2023-03-25T10:32:17.475+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"trace": "java.util.NoSuchElementException: No value present ...",
"message": "No value present",
"path": "/product/5000"
}
더 명확한 에러 응답을 전달하기 위해 스프링이 제공하는 다양한 예외처리 방법을 이용
Spring이 제공하는 다양한 예외처리
Java에서는 예외 처리를 위해 try-catch를 사용해야 하지만 try-catch를 모든 코드에 붙이는 것은 비효율적
Spring은 에러 처리라는 공통 관심사(cross-cutting concerns)를 메인 로직으로부터 분리하는 다양한 예외 처리 방식을 고안하였고, 예외 처리 전략을 추상화한 HandlerExceptionResolver 인터페이스를 만듦(전략 패턴이 사용된 것)
대부분의 HandlerExceptionResolver는 발생한 Exception을 catch하고 HTTP 상태나 응답 메세지 등을 설정
그래서 WAS 입장에서는 해당 요청이 정상적인 응답인 것으로 인식
위의 복잡한 WAS의 에러 전달이 진행되지 않음
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver {
ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex);
}
위의 Object 타입인 handler는 예외가 발생한 컨트롤러 객체
예외가 던져지면 디스패처 서블릿까지 전달되는데, 적합한 예외 처리를 위해 HandlerExceptionResolver 구현체들을 빈으로 등록해서 관리
적용 가능한 구현체를 찾아 예외 처리를 하는데, 우선순위대로 아래의 4가지 구현체들이 빈으로 등록
- DefaultErrorAttributes: 에러 속성을 저장하며 직접 예외를 처리하지는 않음
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver: 에러 응답을 위한 Controller나 ControllerAdvice에 있는 ExceptionHandler를 처리
- ResponseStatusExceptionResolver: Http 상태 코드를 지정하는 @ResponseStatus 또는 ResponseStatusException를 처리
- DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver: 스프링 내부의 기본 예외들을 처리
DefaultErrorAttributes는 직접 예외를 처리하지 않고 속성만 관리하므로 성격이 다름
그래서 내부적으로 DefaultErrorAttributes를 제외하고 직접 예외를 처리하는 3가지 ExceptionResolver들을 컴포지트 패턴을 적용해 HandlerExceptionResolverComposite로 모아서 따로 관리
@ResponseStatus
에러 HTTP 상태를 변경하도록 도와주는 어노테이션으로 다음과 같은 경우 적용
- Exception 클래스 자체
- 메소드에 @ExceptionHandler와 함께
- 클래스에 @RestControllerAdvice와 함께
예시
우리가 만든 예외 클래스에 다음과 같이 @ResponseStatus로 응답 상태를 지정
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class AppException extends RuntimeException {
}
그러면 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver가 지정해준 상태로 에러 응답이 내려가도록 처리
{
"timestamp": "2023-03-25T11:20:41.675+00:00",
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"path": "/product/5000"
}
하지만 에러 응답에서 알 수 있듯이 이는 BasicErrorController에 의한 응답
@ResponseStatus를 처리하는 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver는 WAS까지 예외를 전달시키며, 복잡한 WAS의 에러 요청 전달이 진행되는 방식
한계점
- 에러 응답의 내용(Payload)를 수정할 수 없음(굳이 DefaultErrorAttributes 수정 시 가능)
- 예외 클래스와 강하게 결합되어 같은 예외는 같은 상태와 에러 메세지를 반환
- 별도의 응답 상태가 필요하다면 예외 클래스를 추가해야 됨
- WAS까지 예외가 전달되고, WAS의 에러 요청 전달이 진행
- 외부에서 정의한 Exception 클래스에는 @ResponseStatus를 붙여줄 수 없음
ResponseStatusException
외부 라이브러리에서 정의한 코드는 우리가 수정할 수 없으므로 @ResponseStatus를 붙여줄 수 없으므로, Spring5에서 @ResponseStatus의 프로그래밍적 대안으로써 손쉽게 에러를 반환할 수 있는 ResponseStatusException가 추가
ResponseStatusException는 HttpStatus와 함께 선택적으로 reason과 cause를 추가할 수 있고, 명시적으로 에러를 처리해주지 않아도 되게끔 언체크 예외을 상속
예시
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Product> getProduct(@PathVariable String id) {
try {
return ResponseEntity.ok(productService.getProduct(id));
} catch (NoSuchElementFoundException e) {
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND, "Item Not Found");
}
}
이점
- 기본적인 예외 처리를 빠르게 적용할 수 있으므로 손쉽게 프로토타이핑할 수 있음
- HttpStatus를 직접 설정하여 예외 클래스와의 결합도를 낮출 수 있음
- 불필요하게 많은 별도의 예외 클래스를 만들지 않아도 됨
- 프로그래밍 방식으로 예외를 직접 생성하므로 예외를 더욱 잘 제어할 수 있음
한계점
- 직접 예외 처리를 프로그래밍하므로 일관된 예외 처리가 어려움
- 예외 처리 코드가 중복될 수 있음
- Spring 내부의 예외를 처리하는 것이 어려움
- 예외가 WAS까지 전달되고, WAS의 에러 요청 전달이 진행됨
@ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler는 매우 유연하게 에러를 처리할 수 있는 방법을 제공
다음 항목에 @ExceptionHandler는 어노테이션을 추가함으로써 에러를 손쉽게 처리
- 컨트롤러의 메소드
- @ControllerAdvice나 @RestControllerAdvice가 있는 클래스의 메소드
컨트롤러의 메소드
다음과 같이 컨트롤러의 메소드에 @ExceptionHandler를 추가함으로써 에러를 처리
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public Response getProduct(@PathVariable String id){
return productService.getProduct(id);
}
@ExceptionHandler(NoSuchElementFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<String> handleNoSuchElementFoundException(NoSuchElementFoundException exception) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(exception.getMessage());
}
}
@ExceptionHandler는 Exception 클래스들을 속성으로 받아 처리할 예외를 지정 가능
만약 ExceptionHandler 어노테이션에 예외 클래스를 지정하지 않는다면, 파라미터에 설정된 에러 클래스를 처리
또한 @ResponseStatus와도 결합 가능
만약 ResponseEntity에서도 status를 지정하고 @ResponseStatus도 있다면 ResponseEntity가 우선순위
ExceptionHandler의 파라미터로 HttpServletRequest나 WebRequest 등을 얻을 수 있으며 반환 타입으로는 ResponseEntity, String, void 등 에러 응답(payload)을 자유롭게 활용 가능(높은 유연성)
- code: 어떠한 종류의 에러가 발생하는지에 대한 에러 코드
- message: 왜 에러가 발생했는지에 대한 설명
- error: 어느 값이 잘못되어 @Valid에 의한 검증이 실패한 것인지를 위한 에러 목록
여기서 code로 내부적으로 정의한 값을 사용하는 것보다 BAD_REQUEST와 같은 HttpStatus같은 가독성 좋은 값을 사용하는 것이 명시적으로 좋음
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ProductController {
...
@ExceptionHandler(NoSuchElementFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleItemNotFoundException(NoSuchElementFoundException exception) {
...
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
...
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleAllUncaughtException(Exception exception) {
...
}
}
Spring은 예외가 발생하면 가장 구체적인 핸들러를 먼저 찾고, 없으면 부모 핸들러를 찾음
예를 들어 NullPointerException이 발생했다면, 위에서는 NullPointerException 처리기가 없으므로 Exception에 대한 핸들러를 찾음
@ExceptionHandler에 등록된 예외 클래스와 파라미터로 받는 예와 클래스가 동일하지 않으면 스프링은 컴파일 시점에 에러를 내지 않다가 런타임 시점에 에러를 발생
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No suitable resolver for argument [0] [type=...]
HandlerMethod details: ...
한계점
@ExceptionHandler는 컨트롤러에 구현하므로 특정 컨트롤러에서만 발생하는 예외만 처리
컨트롤러에 에러 처리 코드가 섞이며, 에러 처리 코드가 중복될 가능성이 높음
그래서 스프링은 전역적으로 예외를 처리할 수 있는 다음 기술을 제공
@ControllerAdvice와 @RestControllerAdvice
전역적으로 @ExceptionHandler를 적용할 수 있는 기술
두 개의 차이는 @ResponseBody가 붙어 Json으로 응답
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
...
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestControllerAdvice {
...
}
ControllerAdvice는 여러 컨트롤러에 대해 전역적으로 ExceptionHandler를 적용
위에서 보이듯 ControllerAdvice 어노테이션에는 @Component 어노테이션이 있어서 ControllerAdvice가 선언된 클래스는 스프링 빈으로 등록
그러므로 다음과 같이 에러 처리 위임
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(NoSuchElementFoundException.class)
protected ResponseEntity<?> handleNoSuchElementFoundException(NoSuchElementFoundException e) {
final ErrorResponse errorResponse = ErrorResponse.builder()
.code("Item Not Found")
.message(e.getMessage()).build();
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(errorResponse);
}
}
ControllerAdvice는 전역적으로 적용되는데, @RestControllerAdvice의 basePackages등 설정하면 특정 클래스에만 제한적으로 적용 가능
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler 상속
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler는 Spring MVC에서 발생하는 예외를 처리하는 데 사용되는 추상 클래스
이 클래스는 Spring MVC에서 발생하는 일반적인 예외들을 처리하기 위한 여러 ExceptionHandler가 모두 구현되어 있음
@ControllerAdvice 애노테이션을 사용하여 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler 클래스를 확장하는 클래스를 생성하고, @ExceptionHandler 애노테이션을 사용하여 특정 예외를 처리할 수 있는 메서드를 추가
예를 들어, AppException을 처리하려면 다음과 같은 메서드를 추가
@ExceptionHandler(AppException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> appExceptionHandler(AppException e) {
log.error("AppException : {}", e.getErrorCode());
ErrorResponse errorResponse = new ErrorResponse(e.getErrorCode());
return ResponseEntity.status(e.getErrorCode().getHttpStatus())
.body(Response.error("ERROR", errorResponse));
}
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 사용하면 예외 처리 코드를 작성하는 소요를 줄이고, 모든 예외를 일관된 에러 응답 방식으로 처리할 수 있음
만약 이 추상클래스를 상속받아 사용하지 않는다면, Spring MVC 컨트롤러에서 예외가 발생하면 기본 예외 처리기인 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver클래스가 호출되어 에러 메세지를 반환하지 않는 응답을 반환
스프링 MVC 예외에 대한 명확하고 유용한 에러 메시지를 반환하는 응답을 보내려면 아래 메소드를 오버라이딩해서 사용
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleExceptionInternal(
Exception ex, @Nullable Object body, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) {
if (HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.equals(status)) {
request.setAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex, WebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST);
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, headers, status);
}
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler의 위 메서드는 반환 타입이 ModelAndView가 아닌 ResponseEntity
즉, handleExceptionInternal() 메소드는 응답 형식을 유연하게 재정의 할 수 있고, 일관성 있는 응답 가능
예를 들어, GlobalControllerAdvice가 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 확장하고, Exception만을 처리하도록 설정
@PostMapping으로 명시한 Handler를 DELETE로 요청 테스트
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
}
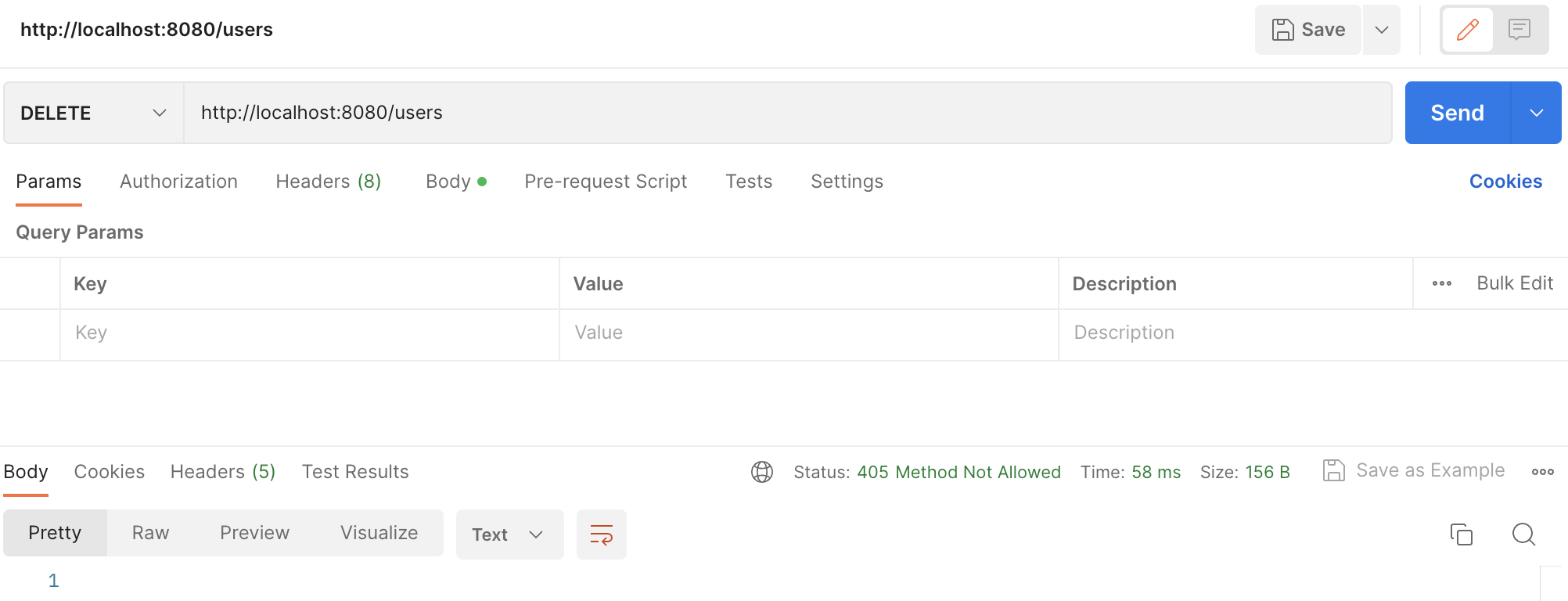
Exception으로 처리되지 않고, Spring MVC Exception이 정상적으로 처리
다만 HTTP Response Body가 존재하지 않기 때문에 명시해주기 위해 다음과 같이 메소드 오버라이딩
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalControllerAdvice extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
private ResponseEntity<ExceptionResponse> handleException(Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Exception : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.internalServerError().body(new ExceptionResponse("예상치 못한 문제가 발생했습니다."));
}
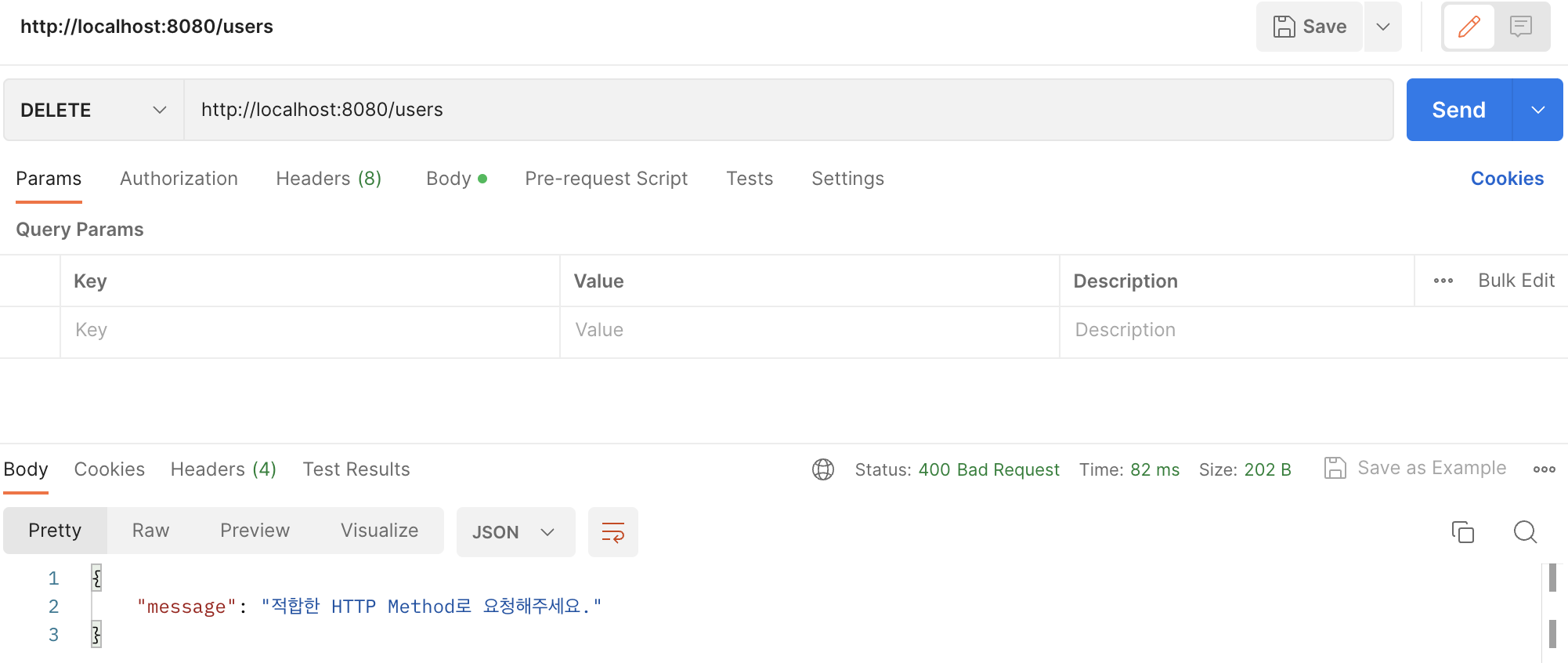
@Override
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException ex,
HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, final WebRequest request) {
logger.info("HttpRequestMethodNotSupported : ", ex);
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(new ExceptionResponse("적합한 HTTP Method로 요청해주세요."));
}
}
댓글남기기